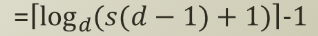문인철 교수님의 ‘데이터 구조 및 분석: Linear Structure and Dynamic Programming’ 수업
Tree as an Abstract Data Type and Structure
Tree as an abstract data type
- data structure operations: insert, delete, search
- special searching 접근 방법: Traverse
why do we use trees?
- 실제 세상에 존재하는 여러 구조들을 분석하는데 좋은 구조임
- ex) 조직도
- 왜 유명한 구조중 하나인가? Divided and Conquer 방법을 이용하여 간단하게 접근할 수 있음
Structure of stored data
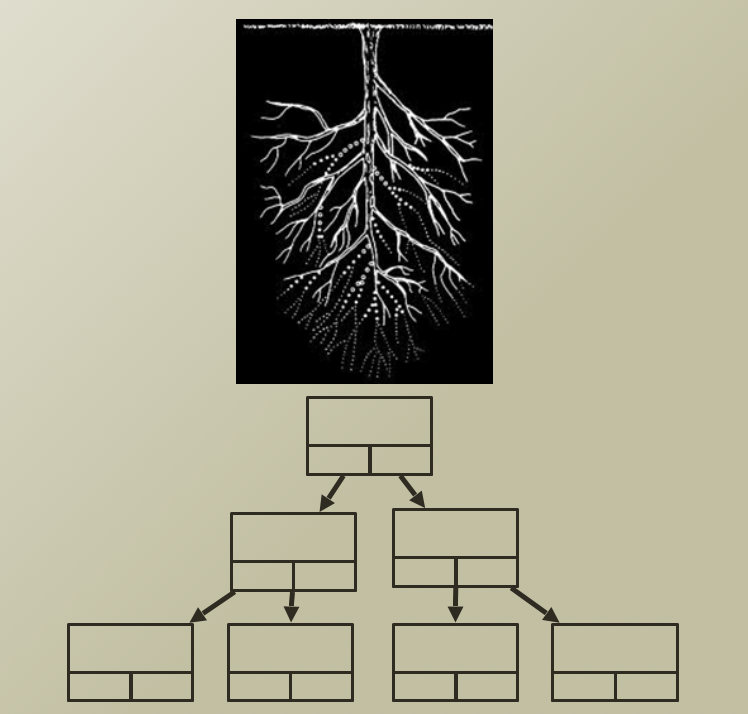
Linked List
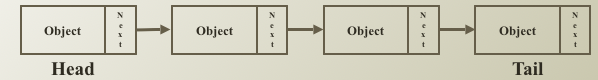
Tree
- 각 노드들은 여러개의 next 노드들을 가지고 있음
- 문제: search 할때 어디서부터 어떻게 찾을지에 대한 고민이 필요함
Terminologies of Tree Structure
Tree Structure 용어 정리
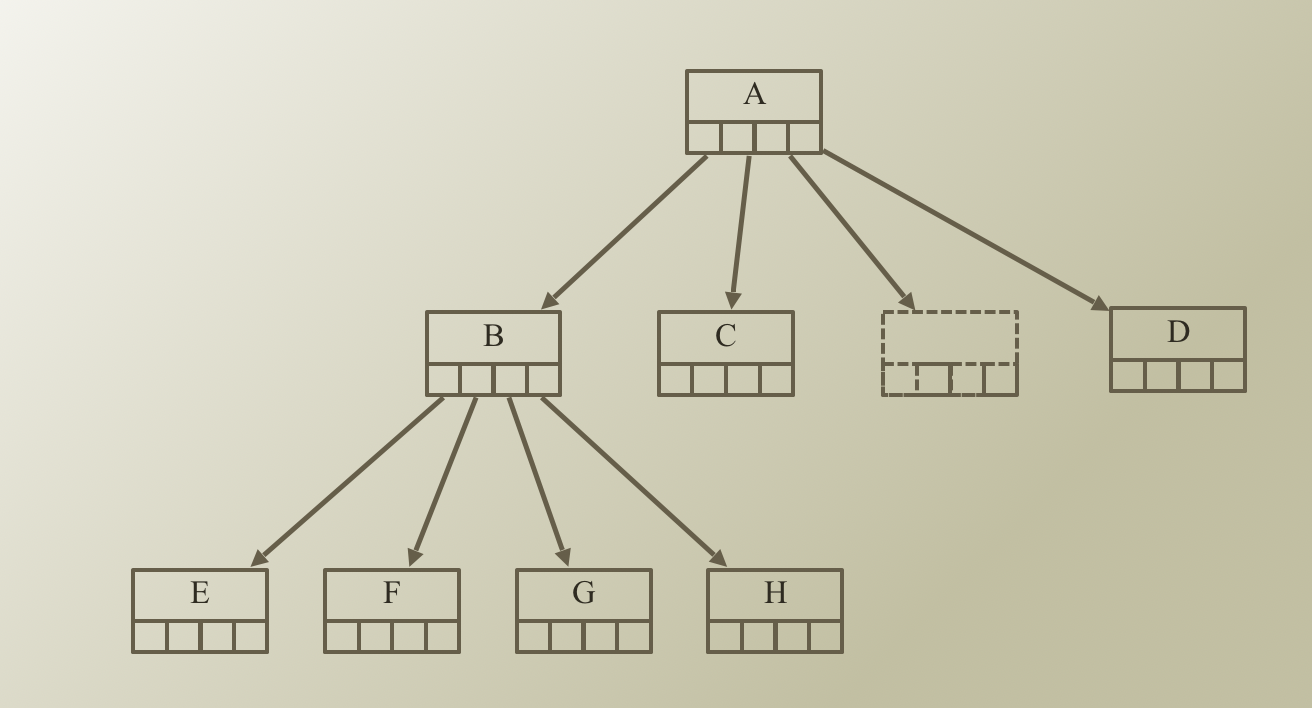
- Root: A
- Edge: 노드를 연결하는 선 (link, branch 라고도 부름)
- Internal Nodes: 자식 노드를 가지고 있는 노드들 (Leaves or terminal nodes 제외)
- ex: A, B, D
- Siblings: 같은 부모 노드를 가지고 있는 노드
- ex: E, F, G, H
- Leves/ Terminal Nodes: 자식 노드를 가지고 있는 않는 노드
- ex: E, F, G, H
- Path: root 부터 특정 노드까지의 최단거리
- Anestors of E: A, B
- Descendants of A: B, C, D, E, F, G, H
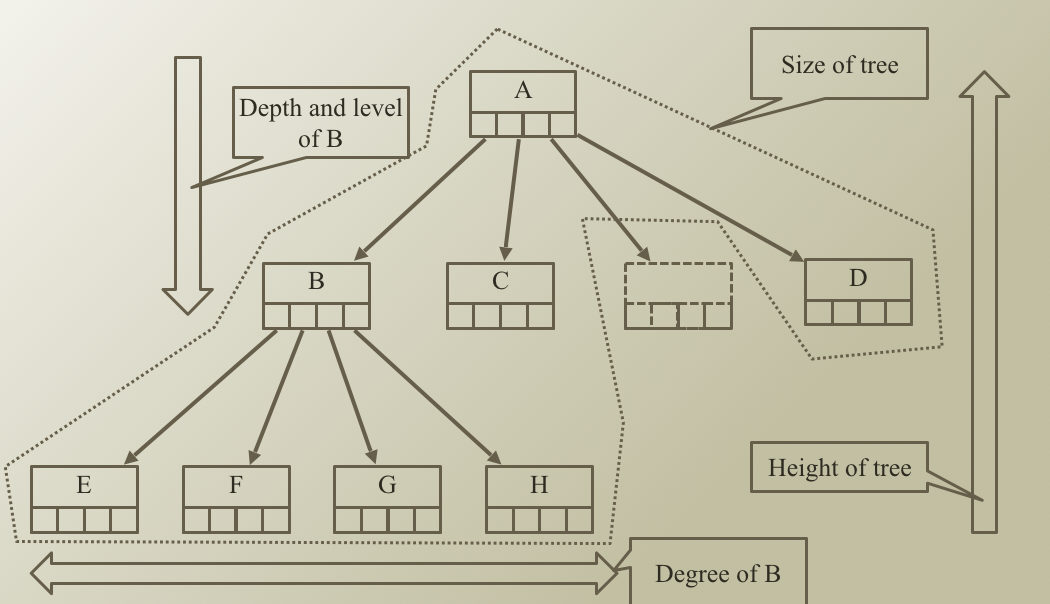
- Size of Tree: 8개
- Depth and level of B: 1
- Degree of B: 4
- Height of Tree: 2
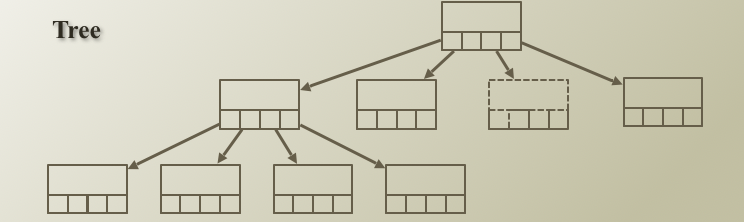
Full Tree
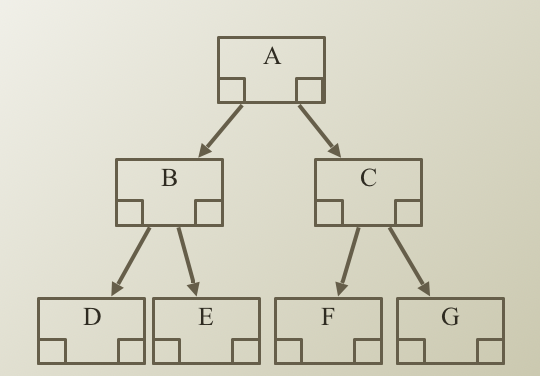
- Leaves 노드를 제외하고 모든 노드들이 자식 노드를 가지고 있음
Complete Tree
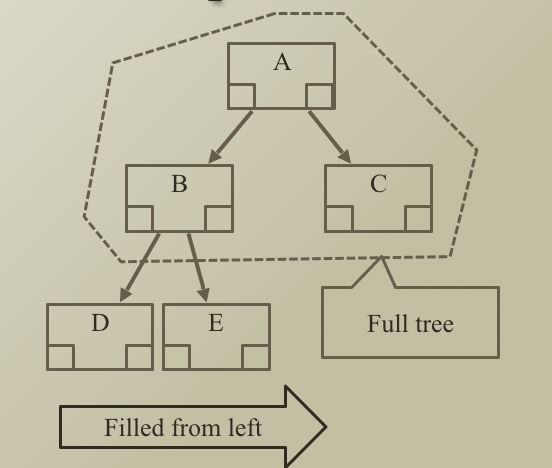
- 위 노드들이 Full tree 이며 왼쪽부터 노드가 채워지면 complete tree 라고 칭함
Characteristics of Tree
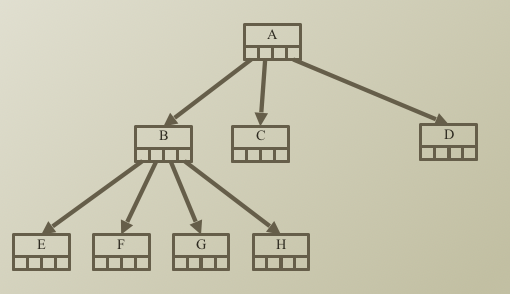
- Edges 개수 = 모든 노드의 개수 - 1 (root노드 제외)
- ex) 8 - 1 = 7
- Depth of root = 0
- Maximum num of nodes at level i with degree d = d^i
- Maximum num of leaves with height h and degree d = d^d
- Maximum size of a tree with height h and degree d
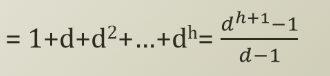
- Height of a complete tree with size s and degree d