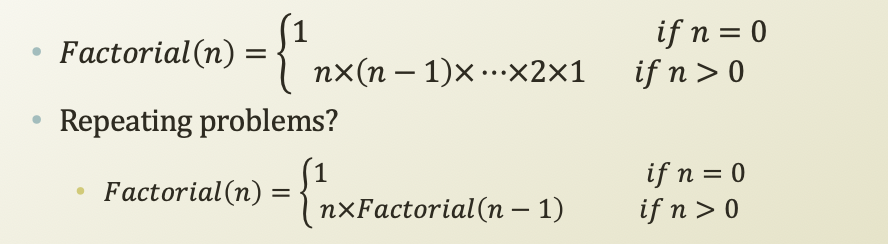문인철 교수님의 ‘데이터 구조 및 분석: Linear Structure and Dynamic Programming’ 수업
Recursions
Repeating Problems and Divide and Conquer
- 큰 문제를 쪼갠 후, 해당 문제를 반복적으로 해결하는 방법
- 동일한 함수를 호출하되, 작게 나누는 것이 포인트
예제
- Factorial
- 최대 공약수
- GCD(A,B) = GCD(B, A mod B)
- GCD(32, 24) = 8
- = GCD(24, 8)
- = GCD(8, 0)
- 정리
- 함수를 반복해서 호출
- Parameters 를 줄임
- 점화식과 비슷 (mathematical induction)
Recursion
- Fibonacci(n) - n = 0, 0 - n = 1, 1 - n≥2 , Fibonacci(n-1) + Fibonacci(n-2)
- 코드
def Fibonacci(n):
if n == 0:
return 0
if n == 1:
return 1
result = Fibonacci(n - 1) + Fibonacci(n - 2)
return result
for i in range(0, 10):
print(Fibonacci(i))
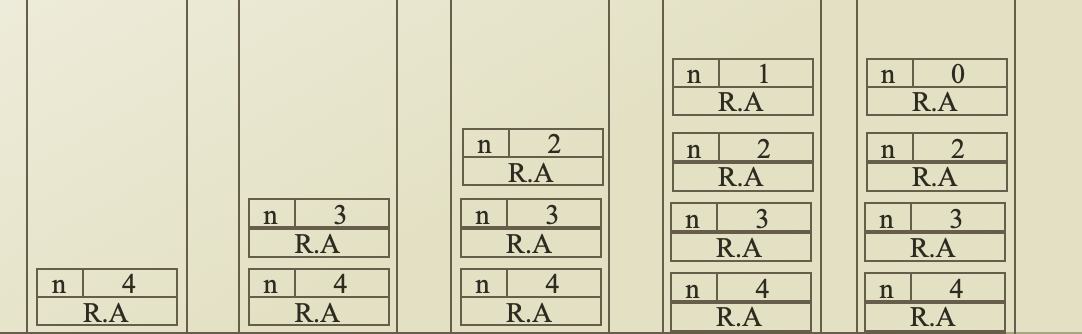
Recursion and Stackframe
- Stackframe is that store your function call history
-
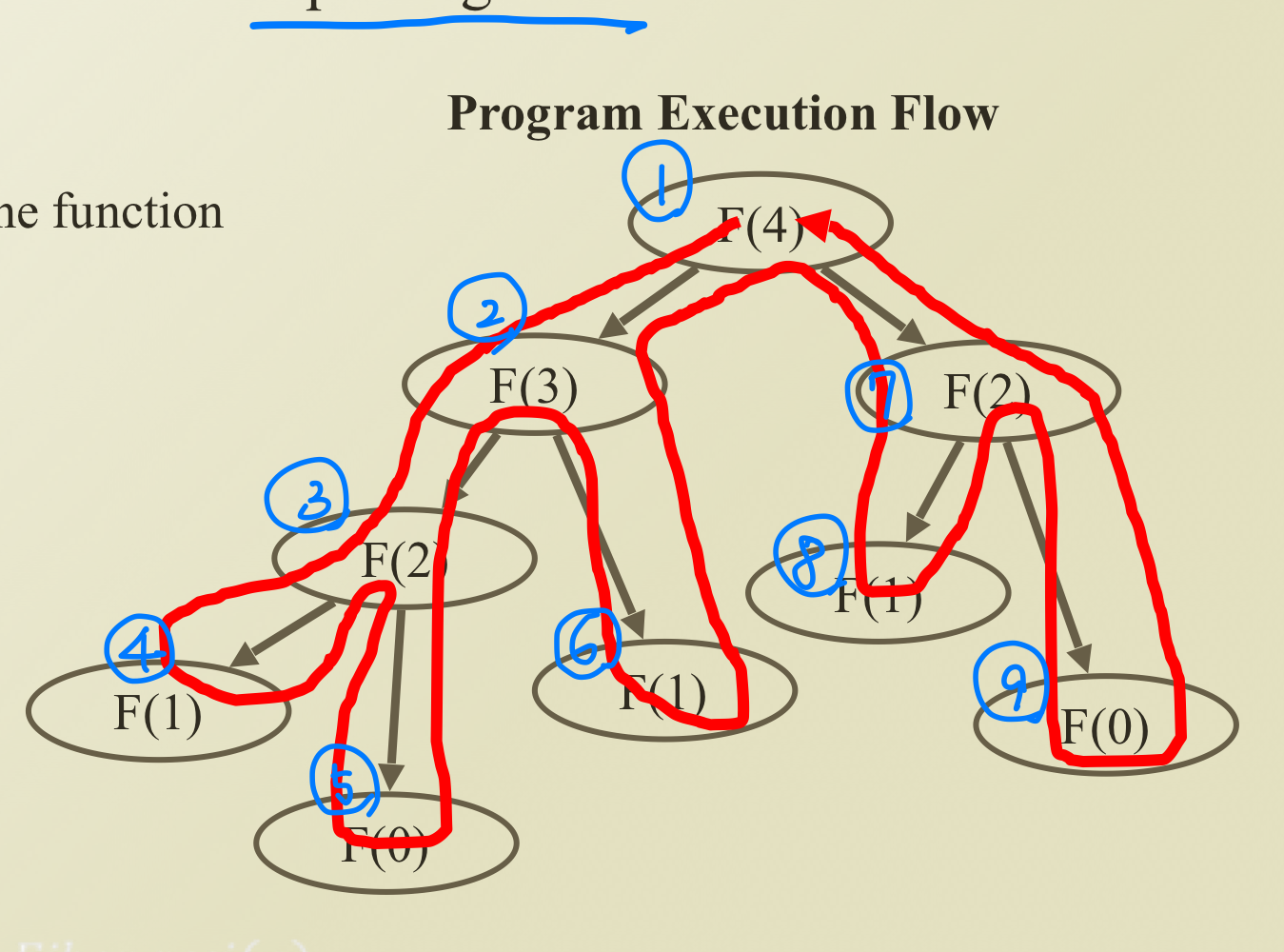 -
-  - push: unction is invoked
- pop: function this return or ends
- 함수호출이 다 끝나면 stackframe 이 비어있
- push: unction is invoked
- pop: function this return or ends
- 함수호출이 다 끝나면 stackframe 이 비어있
Merge Sort
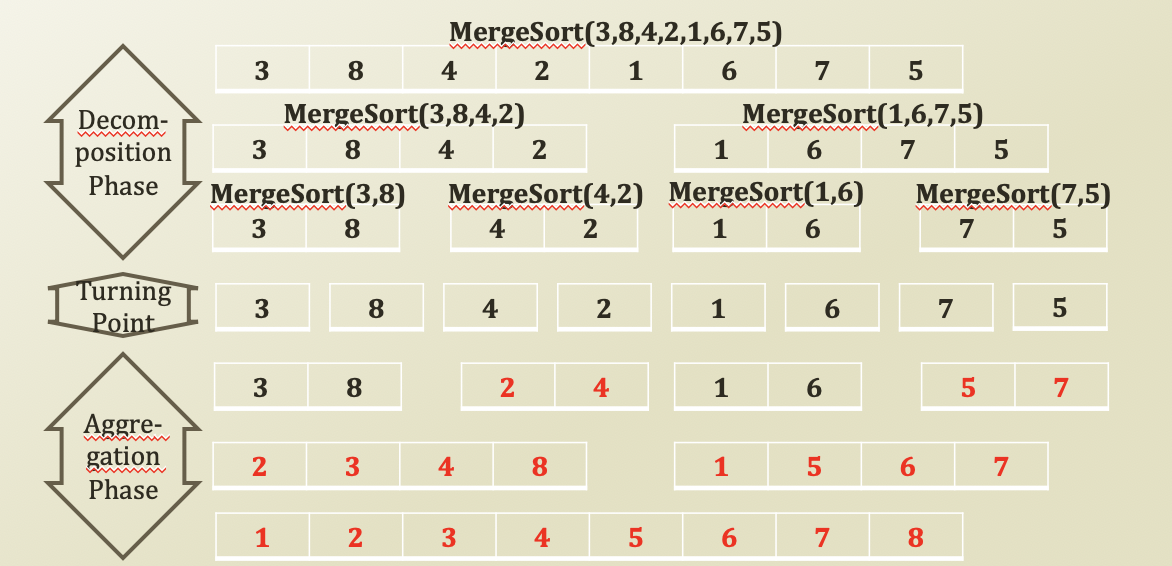
- recursive programming 의 한가지 예
코드
def decompose(list_to_decompose):
list_length = len(list_to_decompose)
sub_list1 = list_to_decompose[:list_length//2]
sub_list2 = list_to_decompose[list_length//2:]
return sub_list1, sub_list2
def aggregate(list_to_sort, sub_list1, sub_list2):
list_length = len(list_to_sort)
idx_count1 = 0
idx_count2 = 0
for i in range(list_length):
if idx_count1 == len(sub_list1):
list_to_sort[i] = sub_list2[idx_count2]
idx_count2 += 1
elif idx_count2 == len(sub_list2):
list_to_sort[i] = sub_list1[idx_count1]
idx_count1 += 1
elif sub_list1[idx_count1] > sub_list2[idx_count2]:
list_to_sort[i] = sub_list2[idx_count2]
idx_count2 += 1
else:
list_to_sort[i] = sub_list1[idx_count1]
idx_count1 += 1
print(f'result = {list_to_sort}')
return list_to_sort
def perform_merge_sort(list_to_sort):
list_length = len(list_to_sort)
if list_length == 1:
return list_to_sort
# decomposition
sub_list1, sub_list2 = decompose(list_to_sort)
print(f'list = {list_to_sort}, sub_list1 = {sub_list1}, sub_list2= {sub_list2}')
# recursion
sub_list1 = perform_merge_sort(sub_list1)
sub_list2 = perform_merge_sort(sub_list2)
# aggregation
result = aggregate(list_to_sort, sub_list1, sub_list2)
return result
실행 결과
import random
list_random = [3, 8, 4, 2, 1, 6, 7, 5]
sorted_list = perform_merge_sort(list_random)
print(sorted_list)
list = [3, 8, 4, 2, 1, 6, 7, 5], sub_list1 = [3, 8, 4, 2], sub_list2= [1, 6, 7, 5]
list = [3, 8, 4, 2], sub_list1 = [3, 8], sub_list2= [4, 2]
list = [3, 8], sub_list1 = [3], sub_list2= [8]
result = [3, 8]
list = [4, 2], sub_list1 = [4], sub_list2= [2]
result = [2, 4]
result = [2, 3, 4, 8]
list = [1, 6, 7, 5], sub_list1 = [1, 6], sub_list2= [7, 5]
list = [1, 6], sub_list1 = [1], sub_list2= [6]
result = [1, 6]
list = [7, 5], sub_list1 = [7], sub_list2= [5]
result = [5, 7]
result = [1, 5, 6, 7]
result = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
Problems in Recursions of Fibonacci Sequence
- 너무 많은 함수 호출 실행
- 중복되는 파라미터로 함수 호출을 진행하는 경우 불필요한 시간, 공간 차지
해결법 → Dynamic Programming, 함수 실행후 결과를 저장해서 중복되는 함수호출을 막는법