Mathematical Expression and Reasoning for Computer Science
Part1. Mathematical Expression
Sets
- 정의
- 집합의 요소라고 불리는 고유 한 개체의 모음
- 한정된 숫자로 이루어지거나 무한히 많은 요소로 이루어질 수 있음
- 표기
-
유한 집합 set: A - 비어있는 set: ∅
-
- 예시
- 유한 집합: {a,b,c,d} , {2,4,-10,3000}
- {(Kahee Yu, 1000000, 52), (Yu, 1000000, 51)}
- 무한 집합
- 자연수: N={0,1,2,…}
- 정수: Z = {…,−2,−1,0,1,2,…}
- 양수: $Z^+ = {1, 2, . . .}$
- rational number, $Q$(유리수)
- real number, $R$ (실수)
- non-negative real number $R^>=0$ - 0,1 을 초과하는 유한 문자열의 경우 $b_1, b_2, b_3$ 이런식으로 표한하고 k는 자연수로서 길이라고 표현. 만약 문자열 길이가 0 빈 문자열인 경우엔 ε 표기 - ${x | x ∈ N and x ≥ 5}$
-
x 는 5와 같거나 작다라는 의미, ( 앞의 부분)은 집합의 변수 x/ 오른쪽 부분은이 변수의 조건 - $Q=\frac{p}{q}$ p,q ∈ Z and q!=0
Operaion on sets
- $x \in A$: True
- $y \notin A$: True y는 set A에 원소로 없기 때문
- $A \subseteq B$: True, A is B의 부분집합
- $A \subseteq A$, $∅ \subseteq B$: Ture
- $A=B$: True, $A \subseteq B$, $B \subseteq A$
- $A \cup B$: union, A and B, A 와 B 모든 요소를 반환
- $A \cap B$: intersection,
- A\B: difference, A의 모든 요소는 A는 있으나 B에는 없음
- A x B: product, pairs (a, b)
- $P(A)$: power set, A의 모든 부분집합
- A= {1,2,3}
- P(A) = {∅, {1}, {2}, {3}, {1, 2}, {1, 3}, {2, 3}, {1, 2, 3}}
Functions
- A function f : A → B: A의 원소에서 B의 원소까지의 매핑
- A: function of domain
- B: funcation of range
- A,B가 자연수라고 가정했을 때 Pred: Z → Z
- Pred(x) = x-1, x 보다 작은 정수를 매핑하는 함수
- mapping: A요소가 한번만 나타나는 카티션 곱(A x B)을 의미한다.
- {…,(−2,−3),(−1,−2),(0,−1),(1,0),(2,1),…}
- function f: A1 × A2 × · · · × Ak → B
- k 개의 인수를 갖는 함수
- 1과 k 사이의 i번째 요소는 반드시 $A_{i}$, f g 함수의 결과값은 반드시 B의 요소여야함
- operator + : R × R → R: 두개의 실수를 입력받은후 이것의 sum을 리턴 = x+y, +(x,y) 표기 할 수 있음
- predicate: {True, False}
- predicate Odd: N → {True, False}, 짝수(even number)는 False 홀수(odd)는 True
- P(x)가 참일 때 x가 P를 만족
- predicate and sests 동등성을 가지고 있음
- predicate P : A → {True, False}
-
set {x x ∈ A and P(x) = True} - P를 만족하는 A 집합
- flip side
- $S \subseteq A$,
- predicate P : A → {True,False}, P(x) = True if x ∈ S, P(x) = False if $x \notin S$.
Summation and product notation
- summation notation
- $\sum_{n=1}^{100} \frac{i+i^2} {3+i}$
- i: index of summation
- 1 ~ 100: lower and upper bounds of summation
- pair of integers j and k, and any function f : Z → R
- $\sum_{i=j}^{k} f(i) = f(j)+f(j+1)….+f(k)$
- product notation to abbreviate multiplication
- $\prod_{i=j}^{k} f(i)=f(j) * f(j+1)* … f(k)$
- j > k $\sum_{i=j}^{k} f(i) = 0$
- j > k $\prod_{i=j}^{k} f(i) = 1$
Inequalities
- Theorem 1.1. a,b,c: 실수, the following are true
- If a≤b and b≤c,then a≤c
- If a≤b,then a+c ≤ b+c
- I fa≤b and c>0,then ac ≤ bc
- If a≤b and c<0,then ac ≥ bc
- If 0 < a ≤ b,then $\frac{1}{a} ≥ \frac{1}{b}$
- If a ≤ b < 0, then $\frac{1}{a} ≥ \frac{1}{b}$
- 음수를 곱하거나 역수 사용하는 경우 the direction of the inequality,
- Definition 1.3. Let f : $R^≥0 → R^≥0$
- f는 strictly increasing
- 조건 $x,y \in {R^≥0}$, if x < y then f(x) < f(y)
- strictly increasing
- f (x) = $x^2$
- f (x) = $log_3(1+x)$
- Exponential functions(지수함수) f (x) = $2^x$
- Theorem 1.2: 음수가 아닌 실수 a,b all strictly increas- ing functions f : $R^≥0 → R^≥0$
- If a≤b,then f(a)≤ f(b).
Propositional logic
- Propositional(명제): 참 거짓의 명령문
- 예시
- Every even integer greater than 2 is the sum of two prime numbers(소수).: False
- propositional variables: p
- propositional/logical operator: 인수 모두 참 또는 거짓 (input이 모두 boolean 이어야한다.)
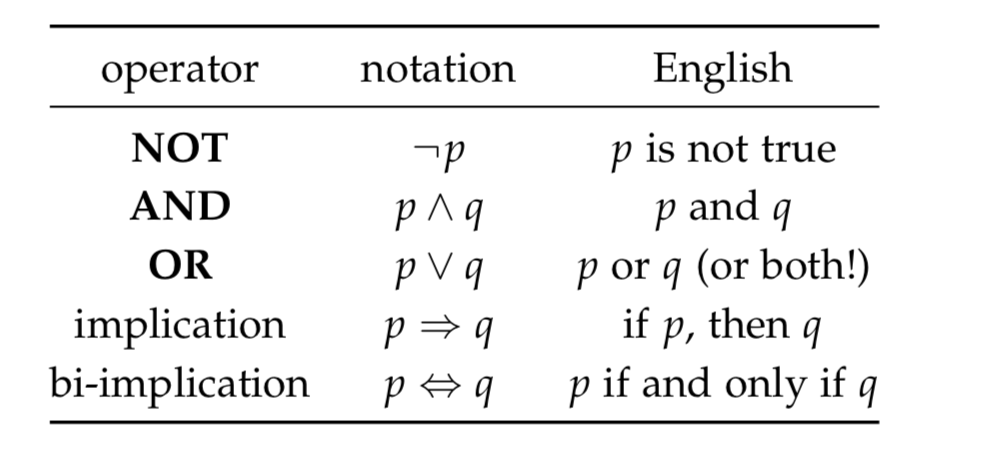
The basic operators: NOT, AND, OR
- NOT, -: if p is Ture then -p is False
- AND, ^: 두개의 인자가 True
- OR, V: 둘중 하나만 True
- AND, OR 은 바이너리 연산자라는 점에서 같음
- first and last months’ rent and a 1000 deposit
- first and last months’ rent or a 1000 deposit
- 두번째 조건이 좀더 저렴하게 렌트비를 낼 수 있는 조건임
The implication operator
- p는 가설, q 결론
- p ⇒ q, p가 True 이면 q도 반드시 True
- p가 False 이면 p ⇒ q 거짓
- p가 False 이고, 가 True 또는 False 일 때 p ⇒ q를 True
- vacuous truth cases: p ⇒ q를 True, p가 Fasle
- 어떻게 이런 판단을 내리는가?
은 p가 False 일 때 q가 발생해야하는지 여부에 대해 아무 것도 말하지 않기 때문에 p가 False 일때 증명할 수가 없음
- 어떻게 이런 판단을 내리는가?
- If you are a Pittsburgh Pens fan, then you are not a Flyers fan
- You are not a Pittsburgh Pens fan, or you are not a Flyers fan(¬p ∨ q: ): p가 거짓이면 p ⇒ q 참이고, p가 참이면 q도 참
- If you are a Flyers fan, then you are not a Pittsburgh Pens fan.(¬q ⇒ ¬p): q가 일어나지 않으면 p도 발생 할 수 없다.
- p ⇒ q , ¬p ∨ q, ¬q ⇒ ¬p 같은 결과값이 나와야한다.
- converse: p ⇒ q를 취하고 가설과 결론을 전환하면 q ⇒ p 를 얻을 수 있다.
Biconditional
- p ⇔ q, p ⇒ q, q ⇒ p 둘다 참일때,(p ⇒ q)∧(q ⇒ p)
- if p then q, and if q then p.” = p iff q
- p:true, q:ture ture
- p:false, q:false false
Summary
문제
- A tautology is a formula that is True for every possible assignment of values to its propositional variable
- 답은 (c)
- a) ((p⇒q)∧(p⇒r))⇔(p⇒(q∧r))
- b) (p⇒q)⇔(¬p∨q)
- c) (¬(p∨q)) ⇔ (¬p∧¬q)